Full container load (FCL) and less than container load (LCL) are terms that are often heard in the highly complicated shipping and logistics scene. An understanding of the differences between FCL and LCL becomes a cost-effective presence in the decision-making strategy of the business in a highly competitive environment such as India. This article elaborates on the definitions of FCL and LCL, the key differences between the two, and the deciding factors in choosing between them. Documentation requirements will be looked after, along with some examples, not to forget sections on how Drip Capital provides customized financial solutions for your shipping needs.
What is FCL and LCL in Shipping?
FCL (Full Container Load)
An FCL (Full Container Load) is a mode of shipping in which a single shipper occupies the entire container with his goods. This mode is adopted for large shipments in which the volume of cargo justifies renting the container as a whole. The other important advantage of FCL shipping is that the container is sealed and kept unopened until the final destination, thus providing increased security and minimum handling.
LCL (Less than Container Load)
LCL (Less than Container Load) applies in a case where the goods from a single shipper do not fill an entire container. In this case, shipments from various shippers are assembled and stuffed into one container. This method is economical for smaller shipments; however, it involves more handling of the cargo, which in turn could increase the risk of damage to the goods.
FCL vs. LCL: Key Factors to Consider
Below is a comparison of the key factors of FCL and LCL to understand which option best suits your shipping needs:
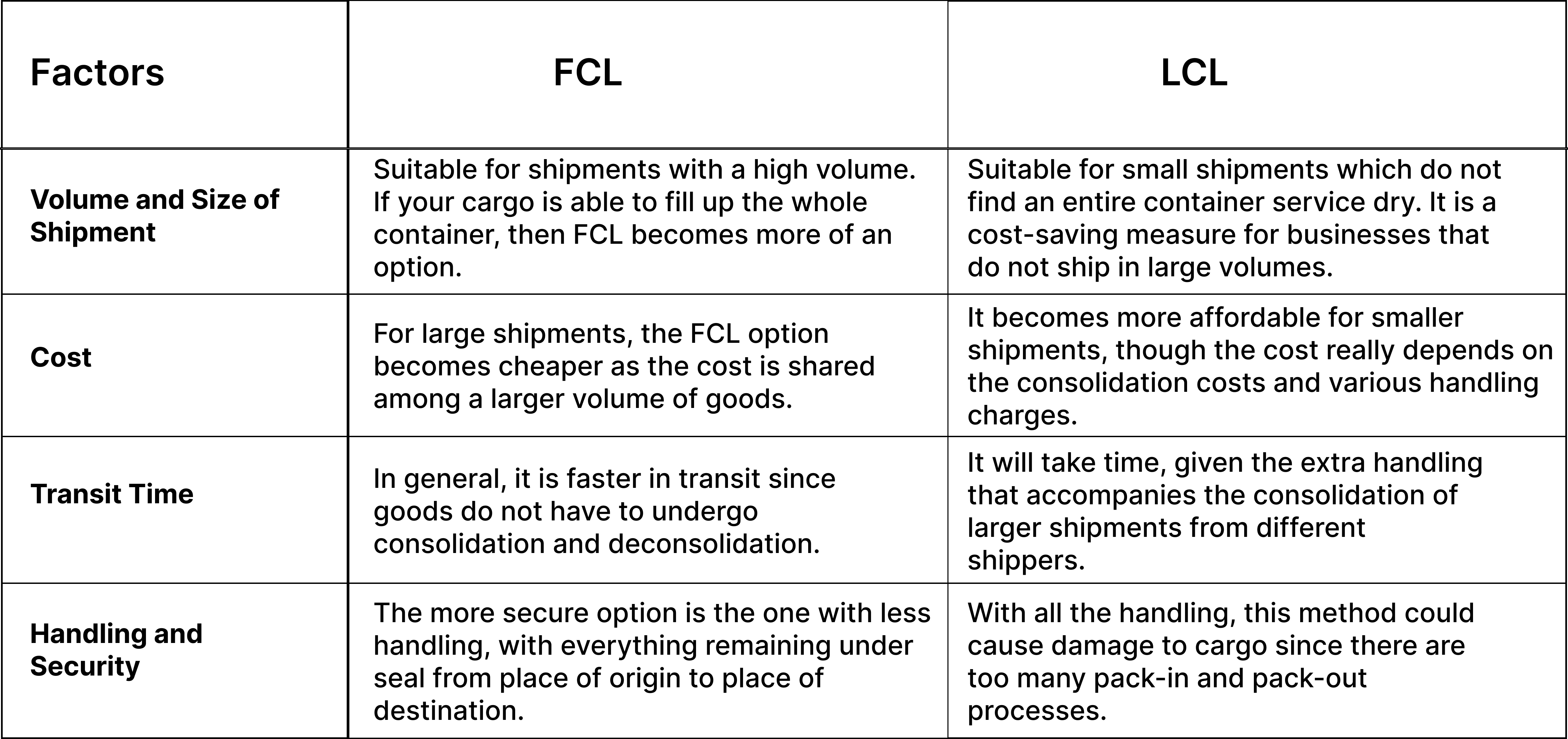
According to a report from the International Transport Intermediaries Club (ITIC), the global shipping industry recorded a 2.6% increase in containerized trade volumes during 2023. Guided Imports has done its study and published the report stating that, in general, for LCL shipments, small companies, especially startups, have a cost advantage of 15-20% over FCL.
Shipa Freight states that by avoiding consolidation and deconsolidation processes, FCL is 10-15% faster than LCL. Mariners Galaxy suggests that the likelihood of damage to FCL cargo is 5% less than that of LCL due to fewer handling operations.
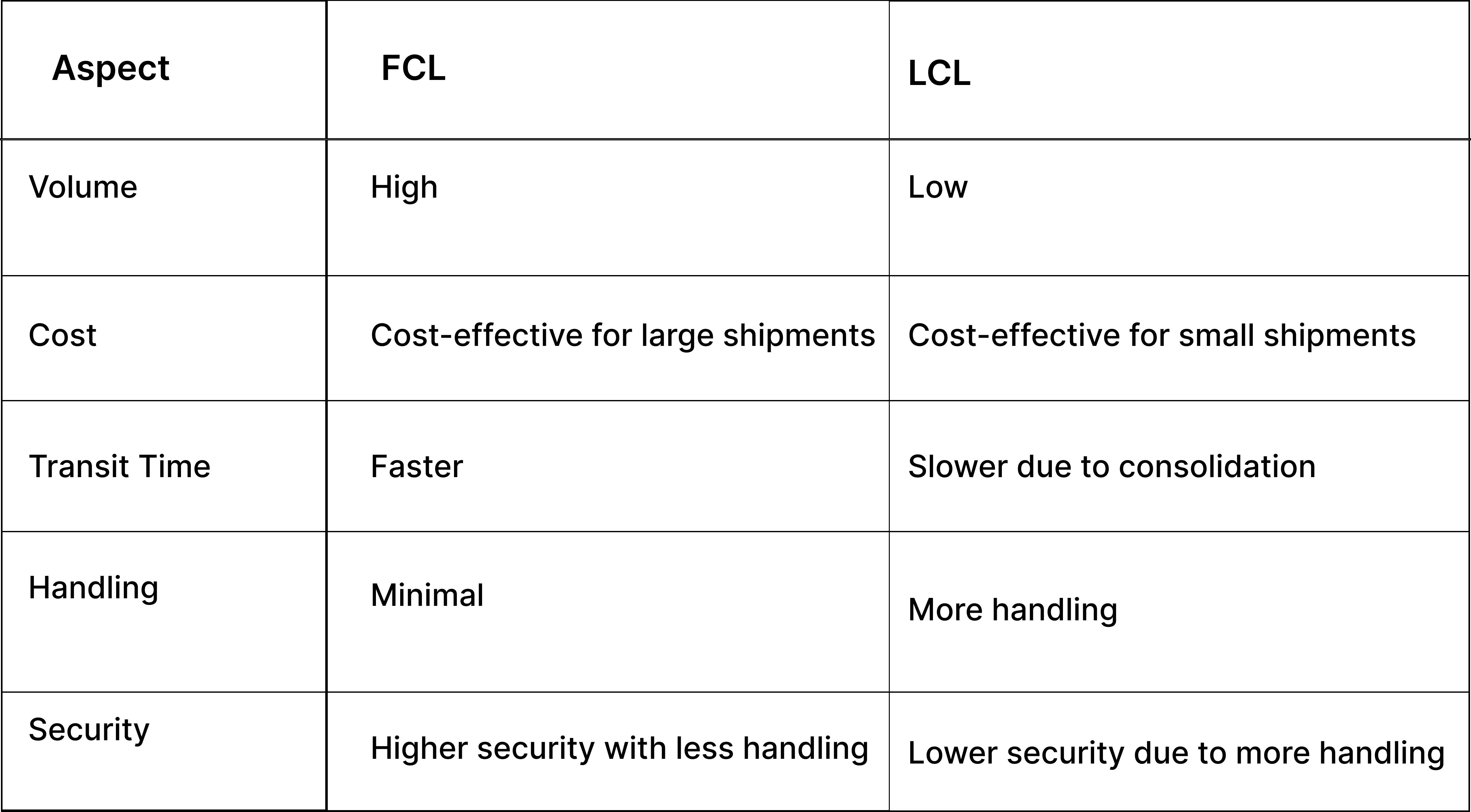
FCL vs LCL: Key Differences
Below are the key differences of FCL vs LCL to help you determine the most suitable option for your shipping needs:
What are the Documents Required for FCL and LCL?
Certain documents are necessary for smooth shipping procedures for FCL and LCL shipments:
- Bill of Lading: A detailed list of a shipment of goods is given here as a receipt by the carrier to the party consigning the goods.
- Commercial Invoice: A document needed by customs to ascertain the value of the goods for duty purposes.
- Packing List: Information relative to the shipment, including the quantity, description, and weight of the cargo.
- Certificate of Origin: A document stating the country in which the goods have been produced, which is important for tariffs and trade agreements.
- Insurance Certificate: This indicates that insurance was taken out on this shipment, protecting it from potential loss.
Examples of FCL and LCL in Shipping
FCL Example
An Indian exporter ships a full container load of textiles to Europe, which remains sealed in India and opened only on arrival at the European port. This guarantees that the goods are safe and secure during transit.
LCL Example
A small business in India is shipping a few pallets of handicrafts to the USA. These products are packed in a container together with other shipments. The LCL method is cheaper for small businesses, but their goods get handled more often through the shipping procedure.
How Can Drip Capital Help?
Drip Capital specializes in various financing solutions to meet your shipping needs. For example, Trade Finance could be of great help to any business engaged in import/export activities. It allows your shipments to receive the required funds so that financial flow will not be interrupted and the business runs smoothly. The Receivable Finance further improves your liquidity by financing your receivables, ensuring that working capital is at hand to cover costs borne for shipping and managing your supply chain adequately.
Also Read: A complete guide on consignor and consignee in shipping
Drip's solutions are tailored to provide Indian businesses with the financial flexibility necessary to manoeuvre through the labyrinth of global trade. Whether FCL or LCL, Drip Capital offers a range of financial products tailoring your requirements.
Various factors determine the choice between FCL vs LCL: shipment volume, costs, transit time, and security requirements. FCL works well for larger shipments while offering the security and faster transit times needed for this mode. LCL would be suitable for smaller shipments, such as those shipping lower volumes and looking for cost-effective solutions. Understanding these differences enables you to maximise your logistics strategy and make informed shipping decisions. In the Indian market, financial solutions from Drip Capital, like Receivable Finance could provide the necessary support to facilitate your shipping processes and seamless operations.
For more information on how Drip Capital can assist you with all your shipping needs, visit Drip Capital.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does 40 FCL mean?
A 40 FCL implies a 40-foot Container Load that is dedicated completely to one shipper's cargo, hence having the advantages of secure shipment and minimal handling.
2. Is FCL the same as LCL?
No. FCL is a complete container load from one shipper, while LCL puts together loads from many shippers into one container. Each move has its benefits and is superior for different shipment volumes and cost purposes.
3. FCL vs. LCL: which is better?
The best solution is up to your unique concerns about shipment size, cost, transit time, and security. Generally, FCL is more appropriate if the consignment is bigger; however, LCL is more suitable for smaller consignments.


